Introduction
User Experience (UX) focuses on the user’s understanding and delivering a seamless experience of all the services provided by the company to the end-user. The UX design is not only about making the product easier to use but also integrating other experiences like marketing campaigns or any other aspects of branding to deliver solutions addressing the needs.
During term 1 of MA Web Design and Content Planning, the two sessions of the User Experience Design module covered UX Research and UX Design which help me understand the importance of researching in designing a good product. As I mostly focused on the coding part of the development, these sessions helped me understand the approaches taken in UX design.
User Experience Research
The first workshop conducted by Steph Troeth was about User Experience Research (UXR) and it covered the steps involved in conducting and analyzing user research. User research is the study of our targeted user’s needs and pain points in order to design products suitable for them. So, we need to gather data from the users in a structured approach.
Research Objectives
Firstly, we need to set a research objective to state a clear goal of your end product and help be on the same page with the whole team. Setting a research objective will also benefit in selecting an appropriate methodology. Steph provided three examples of research objectives which were close-ended, semi open-ended, and open-ended and exploratory. Open-ended research is suitable when you are in the early phase of discovering the problems while close-ended is appropriate when the product is in development and requires user testing.
Methodology
For the research methodology, Steph listed different methods in the class like qualitative vs quantitative research and attitudinal vs behavioral research. Different research methods can be applied at different stages of the design process to keep in check the user’s needs and filter the important problems.
- Qualitative vs Quantitative Research
Qualitative research is used to comprehend concepts or thoughts for an in-depth knowledge of the topic. These are usually done through interviews with open-ended questions, conversations with the users and focus groups, or ethnographic studies. As it does not involve any numerical data, it requires a lot of interpretation.
Quantitative research is research where data can be measured numerically and in graphs to find out patterns of the users or test the assumptions. These can be conducted through a survey with close-ended questions. A large group of respondents results in a more reliable insight.
- Attitudinal vs Behavioral Research
In attitudinal research, you ask the users about their thoughts exploring more on the “why” questions in the form of an interview or customer feedback. Whereas in behavioral research, you observe the user’s interaction and behavior with the product for e.g., A/B testing, or using tools like google analytics.
These researches can then be conducted in various ways which Steph went on to explain further. They can be moderated or unmoderated, in-person or remote, testing in a lab, 1-1 or group sessions, and assumptions and hypotheses.
Research Methods
After learning about the objectives and methodologies, we need to choose a method to collect the required data. Some of the useful ones that I got to learn during the workshops are listed below:
- Usability Testing
The goal of usability testing is to simulate a scenario with the users where they complete a set of tasks. With this method, you can observe if the users face any difficulties while performing the tasks.
- Concept Testing
It is used to test an idea during the early phases of design to evolve further and test its viability. It can be taken in various forms depending on the design phase and is one of the most used research methods.
- Participatory Design Research
Participatory design is also called co-design sessions, where you work closely with the users to come up with a solution. It can either be done in a group or 1-1 sessions. It helps us in recognizing mental models and use cases, pain points, triggers and motivations, and so on.
- Guerilla Research
This method is taken in the streets and provides strangers to test a small prototype and give their thoughts. It helps in targeting a broader audience but is only suitable when the problem and objective of the research are specific.
- Rapid Iterative Research
RITE (Rapid Iterative Testing & Evaluation) means the prototype goes through many updates with each problem identified during testing to find solutions as fast as possible.
Sampling
During the research, we need to figure out the number of people to speak to and the profiles they have. So, near the end of the first workshop, Steph explained the process of selecting user profiles and how we can find out users to research for our project. We were later tasked to create a survey in a group and take turns in interviewing the members from the other group. It was a valuable practice to learn about properly generating questions for the survey and doing interviews.
User Experience Design
The second workshop was about UX Design with Chris How where he explained UX design and the double diamond process, analysis and synthesis, ideation and sketching, and prototyping with lots of on-hand practical sessions.
Double Diamond
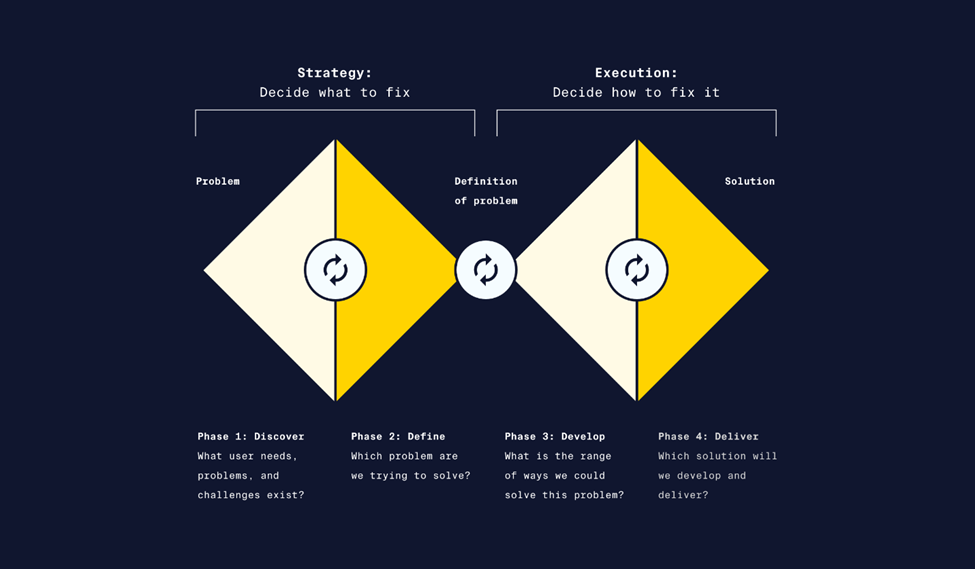
The double diamond method focuses both on the problem and solution to help designers find creative and innovative ideas. It consists of four stages: Discover, Define, Develop, and Deliver. But it is important to note that it is a hypothetical visual model to understand the design process and the process itself can be full of uncertain patterns.
- Discover
The first stage is to do research and explore the problem and the target audience. Just like following the diamond shape, the main focus is to be open and wide to different types of ideas. This can be accomplished through activities like mind mapping and brainstorming.
- Define
The second stage is the convergent part of the diamond where the ideas researched are narrowed down to reach a broad understanding of the problem and leads to the second diamond where the product design takes place. User profiles/stories are a common tool used during this stage.
- Develop
The third stage is the first step in the second diamond or the solution diamond. Like the discovery stage, it takes a divergent approach where designers build prototypes based on the targeted user profiles. Some tools that can be used during this stage are storytelling and journey mapping.
- Delivery
The fourth and final stage is to finalize the prototype and begin testing. After the delivery, the team collects user feedback to improve the product. Surveys are one of the examples for testing.
Analysis and Synthesis
After gathering the research, it needs to be analyzed and synthesized to turn the data into valuable insights by visualizing the data, sorting, or categorizing. Chris listed out four ways that we can visualize the data during the workshop and we were tasked to create some of them during the sessions using the data gathered in the last workshop with Steph. So, the ways we learned to visualize the data were:
- Personas
The first method was to create personas of the people from the research interviews to represent their attitudes and behaviors. This does not have to match exactly with each person but it is a way to help designers and other team members to visualize the type of users they will be designing the product to.
- Job Statements
Job statement works by setting the outcome that the users would be able to achieve by using the product. The method is not about the solution to the problem but rather figuring out the result.
- User Journey Map
A user journey map is a visual diagram that represents the user experience of your site from the initial discovery to the several visits to the website. It helps in understanding how the user interacts with the site and provides the user’s perspective in browsing through your site. This process allows designers to gain insights into pain points and the feelings of the user to further optimize the user experience.
- Empathy Map
The final method that Chris explained and also what we practiced was on an empathy map. The empathy map is divided into four quadrants (says, thinks, does, feels) with a sketch of the user in the center to give an idea to the designers and the team on who the targeted user is. In the task, Chris had us divide the paper into tasks, pain points, feelings, and overall goals. The tasks include what action the user takes, pain points are what the user is thinking throughout their experience, feelings are the user’s emotional state and finally, the goals are well the user would like to achieve.
Ideation and Sketching
In ideation and sketching, we turn our insights from the research into interfaces. There were a few exercises to help us get better at sketching. Mapping the system is one of the activities that we can do to understand the whole flow of the site we are designing. During the session we designed UI flows where you identify each page of the system and the function of that page. You write down what the user may see on the system and draw a line underneath and write what the user can do below the line. This is a fast and easy technique to sketch the flow of the system without having to get into too many details of the page.
Prototyping
The final stage is the prototyping of the insights we gathered from the research. We did the low-fidelity concept sketching in three steps using the Krazy eight technique. First, we do a rapid sketching of eight ideas with just enough clarity to understand the intent of the diagram. Then after reviews and critiques from group members, we do a second round of sketching to improve on the ideas.
We also learned the SCAMPER (substitute, combine, adapt, modify, put to other use, eliminate, and rearrange) technique to help us focus on the improvements that can be done in the third sketching.
Major Project Overview
My project will be to help people interested in the programming field but who are not much aware of the different languages and frameworks that are used in the specific field. As someone who studied BSc IT, I have gone through a similar situation of not knowing what technologies I needed to learn, and even after knowing it, there are currently so many options that a beginner might feel overwhelmed by it. Hence, for that reason, I wanted to create this website where the user has an end goal of the field they want to choose like web, mobile, or even game development. And it will list the languages and frameworks used in that field while also comparing them and helping users decide on the appropriate one. Though for now, it will be only focused on web developments to keep the project feasible within the course year.
Planning
For the research, I will be trying to incorporate both quantitative and qualitative research with methods like usability testing, concept testing, and surveys. The research will mostly be done through remote testing and will be conducted with my friends that usually ask me for help regarding the coding parts and reach out to other people through their help as well. My target audience would be users around their 20s or late teens as I feel that these are the age groups currently interested in this field.
As stated earlier, the project would be focused on web development and I may have some experience with web development, but I still need to do research on my own on other web development frameworks for the content to be trustworthy. The basic content would be about HTML, CSS, and JavaScript then even further advanced information would include JavaScript frameworks like ReactJS, Vue, and Angular while also covering Laravel and Django. I will collect the information for them from the online community and my friends who have experience working on it.
To keep the flow of the project coherent, I will approach the project with the double diamond strategy while designing the user profiles, empathy maps, or maybe even journey maps. For the designing or prototyping aspect, I will be using Figma to design low-fidelity interfaces to get opinions from the surveys and then proceed with high-fidelity prototypes.